はじめに
現状、config.json, device.cert.pem, device.private.key, root.ca.pemなどをdata以下に置いているが、読み取りしか行わないので、NVS領域に置く方が適していると考えられる。(shadow.jsonは書き込みを行うので別)
現状の問題:LittleFSが壊れたら通信不可能
たとえば、ダウンロード処理の不具合などでLittleFSのストレージが溢れた際、証明書の読み込みごと失敗するようになってしまって、どうにもならなくなる可能性があるので、証明書やサーバーの接続情報などはNVS領域に書き込んでおき、そこから読み取るようにしたほうがよい。
以下の記事を参考に、NVS領域に証明書や設定ファイルを書き込むように修正する。ただ、参考記事はESP-IDFフレームワークを利用しているが、今回はPlatformIOを利用しているので、その部分が異なる。
プログラム内の設定の読み込みも現在littlefsから読み取っている箇所をnvsの読み込みに変更する。
全体の方針
- 各種設定ファイルをdata領域から移す(ビルド時にSPIFFS領域に含まれないようにする)
- nvs.csvファイルを作成し、csvファイルを元に、設定ファイルの情報が含まれたcerts.binファイルを生成し、ビルド時にnvs領域にデータを書き込む
- MQTT通信やOTAアップデート時に、LittleFSからではなくcerts.binから証明書データを読み込んで通信確立する。
nvs.binファイルの生成と書き込み
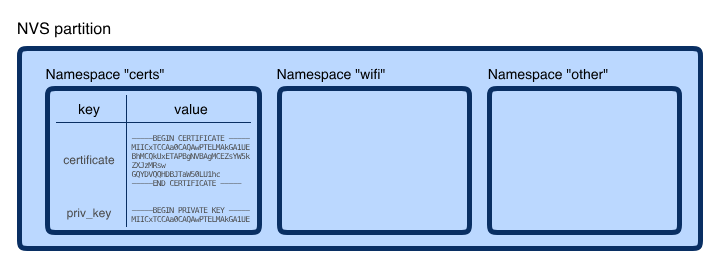
NVSの特徴と名前空間
NVS(Non-Volatile Storage)は不揮発性ストレージの略で、フラッシュ メモリに保存されるキー値データベース。ESP-IDF では、Wi-Fi 認証情報や RF キャリブレーション データなどを保存するために使用される。
デフォルトの NVS パーティションには 16 KB のデータを保存できる。これは、証明書と秘密キーを保存するには十分量なので、カスタム パーティションマップを新しくする必要はない。
また、NVSは名前空間を使用する。キー/値項目を含む NVS パーティション内の「フォルダー」のようなもの。これにより、アプリ、サードパーティのコンポーネント、ESP-IDF 間の競合が防止される。
NVS CSV ファイルの作成
まず、dataディレクトリ配下に設定ファイルを置いたままだと、ビルド時にSPIFFS領域に含まれてしまうので、新しいディレクトリ(certificates)をルートディレクトリ直下に作成して、その中にNVSに含めたい設定ファイルを移動する。
my_project/
├── certificates/
│ ├── config.json
│ ├── device.cert.pem
│ ├── device.private.key
│ ├── root.ca.pem
│ └── nvs.csv
├── include/
├── lib/
├── src/
│ └── main.c
├── platformio.ini
└── ...移動した設定ファイルや証明書を定義するNVS CSVファイル(nvs.csv)をcertificatesディレクトリに作成する。
CSV ファイルの最初のエントリは常にnamespaceエントリである必要があるので、CSVの1行目のtypeはnamespaceにする。また、namespaceのencodingとvalueは空のままにする。
key,type,encoding,value
certs,namespace,,
config,file,string,certificates/config.json
device_cert,file,string,certificates/device.cert.pem
device_key,file,string,certificates/device.private.key
root_ca,file,string,certificates/root.ca.pemflash_nvs.pyスクリプトの作成
NVSパーティションを生成し、フラッシュするためのスクリプトを作成する。
generate_nvs.py:generate_nvs_partition()関数
nvs_partition_gen.pyスクリプトを実行して、certificates/nvs.csvに定義された内容に基づいてcertificates/certs.binというバイナリファイルを生成する。nvs_partition_gen.pyは Espressifによって作成されたコマンドラインツールであり、ESP-IDF に含まれている。
import os
import subprocess
from SCons.Script import Import
Import("env")
def generate_nvs_partition(source, target, env):
print("Generating NVS partition...")
command = [
"python",
os.path.join(os.getenv('IDF_PATH'), 'components', 'nvs_flash', 'nvs_partition_generator', 'nvs_partition_gen.py'),
"generate",
"certificates/nvs.csv",
"certificates/nvs.bin",
"0x5000"
]
result = subprocess.run(command, check=True)
if result.returncode != 0:
print("Error: NVS partition generation failed.")
else:
print("NVS partition generated successfully.")
env.AddPreAction("upload", generate_nvs_partition)flash_nvs.py:flash_nvs_partition()関数
- 生成された
certificates/certs.binをデバイスの0x9000アドレスにフラッシュする(=フラッシュメモリにデータを書き込む)。
import os
import subprocess
from SCons.Script import Import
Import("env")
def flash_nvs_partition(source, target, env):
print("Flashing NVS partition...")
bin_path = os.path.join(env['PROJECT_DIR'], 'certificates', 'certs.bin')
command = [
"python", "-m", "esptool",
"--chip", "esp32",
"--port", env['UPLOAD_PORT'],
"--baud", str(env['UPLOAD_SPEED']),
"write_flash", "0x9000", bin_path
]
try:
result = subprocess.run(command, check=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
print("NVS partition flashed successfully.")
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
print(f"Error: NVS partition flashing failed. Error message: {e.stderr.decode()}")
env.AddPostAction("upload", flash_nvs_partition)ちなみに、現在のpartition tableは下記の設定。nvs: オフセット0x09000から0x5000バイト(20,480バイト)の領域が割り当てられており、通常の設定ファイルや証明書の保存には十分なサイズ。
# Name, Type, SubType, Offset, Size, Flags
nvs, data, nvs, 0x09000, 0x5000,
otadata, data, ota, 0x0e000, 0x2000,
app0, app, ota_0, 0x010000,0x390000,
app1, app, ota_1, 0x400000,0x390000,
spiffs, data, spiffs, 0x790000,0x794000,platformio.iniの更新
platformio.iniファイルを更新して、extra_scriptsとして先ほど生成したpythonコードをpre:generate_nvs.py, post:flash_nvs.pyと追加する。
ビルドプロセスの前にNVSパーティションのバイナリファイルを生成する必要があるのでgenerate_nvs_partition関数はpreスクリプトとして実行する。これにより、ビルド中に必要なすべてのリソースが揃っていることが保証される。
flash_nvs_partition関数はpostスクリプトとして実行する。
アップロードが完了した後に、生成されたNVSパーティションのバイナリファイルをデバイスにフラッシュすることで、アプリケーションコードとNVSデータが確実にフラッシュメモリに存在することが保証される。
[env]
platform = espressif32
framework = arduino
board = esp32dev
lib_deps =
earlephilhower/ESP8266Audio@^1.9.7
extra_scripts = pre:generate_nvs.py, post:flash_nvs.py
board_build.filesystem = littlefs
board_build.partitions = clocky.csv
board_upload.flash_size = 16MB
monitor_speed = 115200
upload_speed = 115200
build_unflags =
-std=gnu++11
build_flags =
-DPIOENV="${PIOENV}"certs.binファイル生成の動作確認
下記は、デバッグ環境でビルドを行い、ファームウェアとNVSパーティションをアップロードし、シリアルモニターを開始するコマンド。
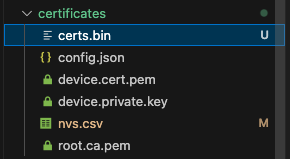
platformio run -e debug --target upload --target monitorビルドが成功した後、certificatesディレクトリ内にcerts.binファイルが生成されていることを確認する。
無事、下記のようにビルド前にcertificatesディレクトリにcerts.bin(20KB)が生成されたことを確認した。
generate_nvs_partition(["upload"], [".pio/build/debug/firmware_debug.bin"])
Generating NVS partition...
Creating NVS binary with version: V2 - Multipage Blob Support Enabled
Created NVS binary: ===> /Users/ky/dev/clocky/clocky_platformio/certificates/certs.bin
NVS partition generated successfully.
Looking for upload port...
....
Writing at 0x002f1146... (97 %)
Writing at 0x002f6479... (98 %)
Writing at 0x002fbc01... (100 %)
Wrote 3074432 bytes (1236860 compressed) at 0x00010000 in 114.0 seconds (effective 215.7 kbit/s)...
Hash of data verified.
Leaving...
Hard resetting via RTS pin...
flash_nvs_partition(["upload"], [".pio/build/debug/firmware_debug.bin"])
Flashing NVS partition...
Using command: python -m esptool --chip esp32 --port /dev/cu.wchusbserial1440 --baud 115200 write_flash 0x9000 /Users/ky/dev/clocky/clocky_platformio/certificates/certs.bin
esptool.py v4.7.0
Serial port /dev/cu.wchusbserial1440
Connecting............
Uploading stub...
Running stub...
Stub running...
Configuring flash size...
Flash will be erased from 0x00009000 to 0x0000dfff...
Compressed 20480 bytes to 3370...
Writing at 0x00009000... (100 %)
Wrote 20480 bytes (3370 compressed) at 0x00009000 in 0.5 seconds (effective 345.5 kbit/s)...
Hash of data verified.Compressed 20480 bytes to 3370…はesptoolがファイルをフラッシュする際にデータを圧縮して送信し、フラッシュメモリに書き込むプロセスを示している。20480 bytes(20KB)のデータが3370 bytes(約3KB)に圧縮されている。フラッシュメモリに書き込む際には、圧縮されたデータが使われるうが、フラッシュメモリ上では実際には20480 bytesが占有される。これはNVSパーティションのサイズがちょうど0x5000バイト(20,480バイト)なので、容量としてはぴったり収まる計算になる。
ただし、これは非常にギリギリのサイズであり、少しでもデータが増えるとすぐに容量不足になるので、少し余裕を持たせて、nvsのサイズを0x6000バイト(24,576バイト)に変更しておくことを検討する。
ただ、その場合、ESP32のパーティションオフセットは通常、0x10000の倍数に配置する必要があるため、app0パーティションのオフセットが0x11000ではなく、0x20000にする必要があり、結構隙間が空いてしまうのが問題になる(SPIFFS領域にできるだけデータを入れたい)ので、一旦このままで。
nvs.binから設定ファイル読み取る
上記で、ESP32にnvs.binをフラッシュできたので、次はnvs.binからデータを読み取る部分を実装する。
NVSの初期化と読み取りの関数を実装
NVSの初期化と読み取りを行う、ヘッダーファイルとソースファイルを作成。必要なESP-IDFのヘッダーをインクルードする。
- #include <nvs_flash.h>
- #include <nvs.h>
// nvs_helper.h
#pragma once
#include <nvs_flash.h>
#include <nvs.h>
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <tl/expected.hpp>
#include <memory>
class NVSHelper {
public:
static tl::expected<void, String> initNVS();
static tl::expected<String, String> readNVS(const char* namespace_name, const char* key);
};- NVSの初期化:
initNVS関数を追加してNVSの初期化を行う。必要に応じてフラッシュメモリの消去を行う。 - NVSからの読み取り:
readNVS関数を追加して、指定されたキーからNVSの値を読み取る。NVSハンドルを開き、値のサイズを取得し、値を読み取る。
#include "nvs_helper.h"
tl::expected<void, String> NVSHelper::initNVS() {
esp_err_t err = nvs_flash_init();
if (err == ESP_ERR_NVS_NO_FREE_PAGES || err == ESP_ERR_NVS_NEW_VERSION_FOUND) {
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(nvs_flash_erase());
err = nvs_flash_init();
}
if (err != ESP_OK) {
return tl::make_unexpected("Failed to initialize NVS");
}
return {};
}
tl::expected<String, String> NVSHelper::readNVS(const char* namespace_name, const char* key) {
nvs_handle_t my_handle;
esp_err_t err = nvs_open(namespace_name, NVS_READONLY, &my_handle);
if (err != ESP_OK) {
return tl::make_unexpected("Failed to open NVS handle");
}
size_t required_size;
err = nvs_get_str(my_handle, key, NULL, &required_size);
if (err != ESP_OK) {
nvs_close(my_handle);
return tl::make_unexpected("Failed to get size of NVS value");
}
std::unique_ptr<char[]> buf(new char[required_size]);
err = nvs_get_str(my_handle, key, buf.get(), &required_size);
if (err != ESP_OK) {
nvs_close(my_handle);
return tl::make_unexpected("Failed to get NVS value");
}
nvs_close(my_handle);
return String(buf.get());
}NVSからデータを読み取る部分を修正
今までLittleFSから設定ファイルを呼び出していた部分を、NVSHelper::readNVS関数を使用して、NVSから呼び出すように修正していく。
例えば、下記のappconfig.cppは今までは下記のようにLittleFSから呼び出していた。
// src/app_config.cpp
#include "app_config.h"
tl::expected<void, String> AppConfig::load() {
File file = LittleFS.open("/config.json", "r");
if (!file) {
LittleFS.end();
return tl::make_unexpected("Failed to open config file for reading");
}
const size_t size = file.size();
std::unique_ptr<char[]> buf(new char[size]);
file.readBytes(buf.get(), size);
const String jsonStr(buf.get(), size);
file.close();
auto result = deserializeAppConfig(jsonStr);
if (result) {
_config = result.value();
return {};
} else {
return tl::make_unexpected(result.error());
}
}下記のように変更する
// src/app_config.cpp
#include "app_config.h"
#include "nvs_helper.h"
tl::expected<void, String> AppConfig::load() {
auto init_result = NVSHelper::initNVS();
if (!init_result) {
return tl::make_unexpected(init_result.error());
}
auto read_result = NVSHelper::readNVS("certs", "config");
if (!read_result) {
return tl::make_unexpected(read_result.error());
}
const String jsonStr = read_result.value();
auto result = deserializeAppConfig(jsonStr);
if (result) {
_config = result.value();
return {};
} else {
return tl::make_unexpected(result.error());
}
}OTAアップデートで、rootCAを読み取る部分も同様に修正(LittleFS→NVS)
// src/ota_update.cpp
#include "nvs_helper.h"
String readRootCA() {
auto init_result = NVSHelper::initNVS();
if (!init_result) {
Serial.println(init_result.error());
return String();
}
auto read_result = NVSHelper::readNVS("certs", "root_ca");
if (!read_result) {
Serial.println(read_result.error());
return String();
}
return read_result.value();
}main.cppで初回起動後にMQTT通信する部分も修正
// src/main.cpp
void setup(){
// 再作成時に利用するので、以下の文字列はメモリを解放しない
auto rootCAResult = NVSHelper::readNVS("certs", "root_ca");
auto clientCertResult = NVSHelper::readNVS("certs", "device_cert");
auto privateKeyResult = NVSHelper::readNVS("certs", "device_key");
auto mqttClient = std::make_unique<MqttClient>(mqttConfig.host,
mqttConfig.port,
const_cast<char*>(rootCAResult.value().c_str()),
const_cast<char*>(clientCertResult.value().c_str()),
const_cast<char*>(privateKeyResult.value().c_str()),
deviceInfo.id);
}動作確認
ESP32をビルドして、起動時に証明書など設定ファイルやキーをNVS領域から読み取ってMQTT通信できるかを確かめる。
16:59:22.451 > [ 51900][V][ssl_client.cpp:68] start_ssl_client(): Starting socket
16:59:22.478 > [ 51924][V][ssl_client.cpp:146] start_ssl_client(): Seeding the random number generator
16:59:22.487 > [ 51933][V][ssl_client.cpp:155] start_ssl_client(): Setting up the SSL/TLS structure...
16:59:22.497 > [ 51943][V][ssl_client.cpp:178] start_ssl_client(): Loading CA cert
16:59:22.507 > [ 51953][V][ssl_client.cpp:234] start_ssl_client(): Loading CRT cert
16:59:22.516 > [ 51963][V][ssl_client.cpp:243] start_ssl_client(): Loading private key
16:59:22.528 > [ 51974][V][ssl_client.cpp:254] start_ssl_client(): Setting hostname for TLS session...
16:59:22.536 > [ 51982][V][ssl_client.cpp:269] start_ssl_client(): Performing the SSL/TLS handshake...
16:59:23.733 > [ 53179][D][ssl_client.cpp:282] start_ssl_client(): Protocol is TLSv1.2 Ciphersuite is TLS-ECDHE-RSA-WITH-AES-128-GCM-SHA256
16:59:23.744 > [ 53191][D][ssl_client.cpp:284] start_ssl_client(): Record expansion is 29
16:59:23.750 > [ 53197][V][ssl_client.cpp:290] start_ssl_client(): Verifying peer X.509 certificate...
16:59:23.759 > [ 53205][V][ssl_client.cpp:298] start_ssl_client(): Certificate verified.
16:59:23.766 > [ 53212][V][ssl_client.cpp:313] start_ssl_client(): Free internal heap after TLS 153048
16:59:23.774 > [ 53220][V][ssl_client.cpp:369] send_ssl_data(): Writing HTTP request with 143 bytes...
16:59:23.876 > connected to AWS IoT
16:59:23.876 > MQTTPubSubClient::subscribe: $aws/things/device_id/shadow/get/accepted無事、動作確認できた。
ただ、今のままでは証明書や秘密鍵などはその気になればユーザーが読み取れてしまう(esptool.pyなどでダンプ可能)ので、秘匿した方が良く、NVS領域のデバイス証明書を暗号化・セキュアブートの有効化も行う必要があるので、今後対応する。



