Introduction.
Explain a scenario where there are two different services (e.g., service A and service B), each with its own docker-compose.yml file, and each with its own app anddb.
The goal here is to allow service A’s app to access service B’s db. In this example, we assume that both services use a common network called my-custom-network.
Creating an existing Docker network
First, we need to manually create an existing Docker network. Use the following command in a terminal to create a network named my-custom-network.
docker network create my-custom-networkThis network is intended to be shared between different docker-compose.yml files.
Before launching a service using the docker-compose.yml file, it must be run individually in a terminal. This allows containers to be launched from different docker-compose.yml files to communicate with each other in the same network.
Using the external: true setting in docker-compose.yml
Next, create a docker-compose.yml file containing the external: true setting.
This setting is used to connect the service to the my-custom-network already created.
For simplicity, we assume that Service A uses MySQL (default port 3306) as the database: and Service B uses PostgreSQL (default port 5432) as the database.
docker-compose.yml for service A
version: '3'
services:: app-a:: apps:: services:: services:: services:: services:: services
app-a:: container_name: app_a_container
container_name: app_a_container
image: app-a:latest
ports:
- "8000:8000"
db-a:
container_name: db_a_containe r
image: mysql:8.0
environment:
MYSQL_DATABASE: db_a_databas e
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: password
ports: "33060:33060:33060
- "33060:3306"
networks: my-custom-net
my-custom-net:
external: true
name: my-custom-networkdocker-compose.yml for service B
version: '3'
services:: app-b:: '3', '3', '3', '3
servic es: app-b:
container_name: app_b_container
image: app-b:latest
ports:
- "8100:8100"
db-b:
container_name: db_b_containe r
image: postgres:latest
environment: postgres:latest
POSTGRES_DB: db_b_databas e
POSTGRES_USER: user
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: password
ports:
- "54320:5432"
networks: my-custom-net:: my-custom-net:: my-custom-net
my-custom-net::my-custom-net
external: true
name: my-custom-networkExample ofdocker psoutput state
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
<id> app-a:latest " docker-entrypoint... " 12 seconds ago Up 11 seconds 0.0.0.0:8000->8000/tcpapp_a_container
<id> mysql:8.0 " docker-entrypoint... " 13 seconds ago Up 12 seconds 0.0.0.0:33060->3306/tcpdb_a_container
<id> app-b:latest " docker-entrypoint... " 10 seconds ago Up 9 seconds 0. 0.0.0:8100->8100/tcpapp_b_container
<id> postgres:latest " docker-entrypoint... " 11 seconds ago Up 10 seconds 0.0.0.0:54320->5432/tcpdb_b_containerURL to access the application
- Application for Service A:
http://localhost:8000 - Application for Service B:
http://localhost:8100
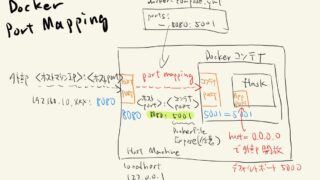
These URLs are based on the port mappings specified in the docker-compose.yml file. The port on the host machine (left side) is forwarded to the port in the container (right side).
Docker port mapping was previously described in this article.
How do I access Service B’s database from Service A?
To connect from an application in service A to a PostgreSQL database in service B, use the following connection information
- Hostname:
db_b_container(database container name for Service B) - Port number:
5432(the internal port that service B listens on default port for PostgreSQL) - Database name:
db_b_database - User name:
user(or PostgreSQL user name set in an environment variable) - Password:
password(password set in environment variable)
The name ofdb_b_containercan be used directly as the hostname for communication between containers, since it is through the external network my-custom-network. The internal port is used directly for inter-container communication, regardless of the port mapping of the host.
The database connection information is as follows
DATABASE_URL = "postgresql://user:password@db_b_container:5432/db_b_database"Behavior oflocalhost in Docker containers
Note that even if we set DATABASE_URL=postgresql://root:password@localhost:5432/db_b_database here, we cannot connect to the Service B database.
In a situation where an application (Service A) and a database (Service B) are running using a Docker container, localhostrefers to the loopback address inside that particular container (i.e., the container itself ).
If you try to connect to something using localhost when service A’s application is running inside a Docker container, it will try to connect inside that same container where service A’s application is running, so service B, let alone service A’s database, not to mention Service B.
Connection from Service B to Service A database
Similarly, when connecting from an application in Service B to a MySQL database in Service A, the database container name ( db_a_container) of Service A is used as the hostname, and the internal port ( 3306 ) on which the database listens is used.
The database connection information for Service A is as follows
DATABASE_URL=mysql://root:password@db_a_container:3306/db_a_databaseConclusion
For communication between Docker containers, use the container name as the hostname and specify the appropriate internal port number. This is because Docker’s internal DNS will automatically resolve the container name to that container’s IP address.
The port mapping defined in docker-compose.yml (e.g., 54320:3306 ) is used for access from outside the container (e.g., host machine). For inter-container communication, the internal port of the service is used directly instead of this external port (54320).
Docker memorandum] Regarding DockerFile, docker-compose.yml, and Docker commands, click here.




コメント