- Introduction.
- Cidacure is currently low on 2000 JAU tablets.
- Why is it held under the tongue for 1 minute and then swallowed?
- Why is it important to refrain from gargling or eating or drinking for 5 minutes after taking a dose?
- Side effects are most common within the first month of administration.
- The mechanism of efficacy of desensitization therapy has not been elucidated.
- At the end.
Introduction.
When I was in Kagoshima, I did not remember suffering from hay fever (the volcanic ash from Sakurajima sometimes burned my eyes if I wore contact lenses), but since coming to Tokyo after college, hay fever has become worse every year.
The dermatologist told me that I might be able to do sublingual immunization, so I did a specific IgE antibody test and got the following results.
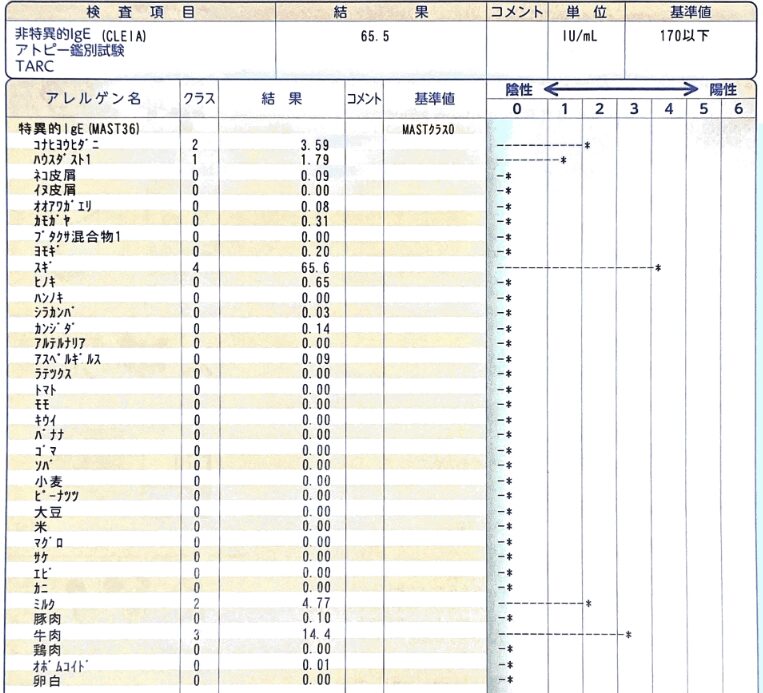
Sure enough, the cedar was stuck, so we decided to start a fern cure.
Beef and milk were also caught, which was surprising, although I don’t recall any symptoms.
I am currently taking 2000 JAU tablets for the equivalent of the first week.
I was given instructions on how to take the tablets, and various questions came to mind, so I did some research.
Cidacure is currently low on 2000 JAU tablets.
Cidacure is a sublingual allergen immunotherapy drug for allergic rhinitis caused by cedar pollen. The dose is 2,000 JAU tablets for the first week and 5,000 JAU tablets for the second and subsequent weeks.
This is done to minimize the risk of side effects by starting with low concentrations first, while allowing the body’s immune system to become accustomed to the allergen.
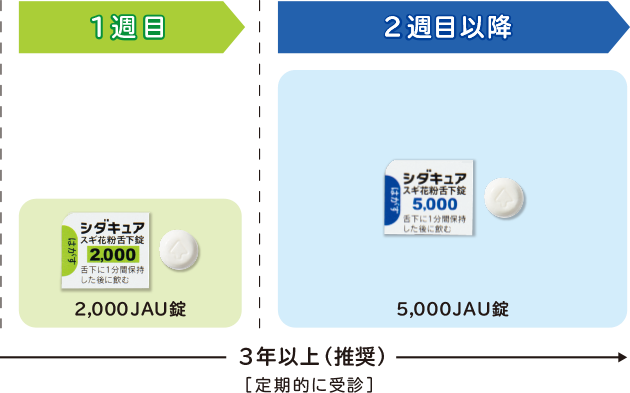
However, as clearly stated in the notice from the Japanese Otorhinolaryngological Society, Cidacure is currently in limited shipment of 2000 JAU tablets, and even if there are patients who wish to receive sublingual immunization, they may not be able to start due to lack of stock.
The 5000 JAU tablets are used more often in the maintenance phase, so it would be understandable if these are in short supply due to excessive demand, but I wonder why the 2000 JAU tablets, which are only used for the first week of dosing, are being shipped in limited quantities. Torii Pharmaceutical’s description included the following
Since it will take a certain period of time to establish a system to significantly increase production, we will continue limited shipments of “Cidacure 2,000JAU” (formulation for increased volume) in 2024. We currently expect that the volume of shipments from our company to our distributors will be the same as in 2023.
We expect that the limited shipments will be cancelled in 2025 or later.
If you want to start sublingual immunization, it would be better to start early because there is a possibility that the above 2000 JAU tablets are not in stock and you cannot start, and also because I think that starting as early as possible after the end of hay fever will reduce symptoms more during the next year’s hay fever season.
Incidentally, “JAU” stands for “Japanese Allergy Units. This is a unit used to indicate the allergen content of drugs used in allergy treatment, especially in Japan.
The reason why 5,000 JAU tablets are used for the maintenance phase is that the efficacy was comparable to that of the 10,000 JAU group in the clinical trial, and therefore, 5,000 JAU tablets are considered to be sufficient.
Why is it held under the tongue for 1 minute and then swallowed?
Cidacure is a fast-dissolving sublingual tablet containing cedar pollen extract, as its name suggests Sublingual Immunotherapy (SLIT), and is a hyposensitization (allergen immunotherapy) drug for cedar pollen allergy.
The dose is held under the tongue for one minute and then swallowed.
It is fast-dissolving, so it dissolves and disappears with saliva the moment it is put in, but saliva should not be swallowed immediately; it must be held under the tongue for one minute.
Why is it necessary to hold for one minute? There are three main reasons for this.
Promotes immune response
- The sublingual area is rich in lymphoid tissue, an environment conducive to triggering an immune system response. The direct contact of allergens with the immune system through the mucosa under the tongue helps the body build tolerance to the allergen.
Efficient absorption
- The sublingual mucosa is rich in blood flow, and allergens are easily absorbed directly into the bloodstream, allowing the allergens to reach the immune system more efficiently. This allows the immune response necessary to suppress allergic reactions to occur faster and more effectively.
Reduction of side effects
- Holding it under the tongue for a certain amount of time prevents the entire allergen from rapidly entering the gastrointestinal tract. This reduces gastrointestinal-related side effects (e.g., nausea and stomach pain).
The value that balances the above efficacy and side effects is one minute, and has been determined as a value based on clinical data. Certainly, it is almost impossible to keep it under the tongue for more than 1 minute, or the patient’s burden is likely to increase.
Why is it important to refrain from gargling or eating or drinking for 5 minutes after taking a dose?
This is also due to two reasons: effectiveness and safety.
To ensure efficient absorption of allergens
The process of allergen absorption into the bloodstream through the sublingual mucosa requires a certain amount of time. Gargling, eating, or drinking may cause allergens administered under the tongue to be washed away or swallowed, and the exact amount needed may not be absorbed.
To reduce the risk of side effects
Avoiding allergens from entering the esophagus and stomach directly reduces gastrointestinal-related side effects (e.g., nausea and stomach pain)
The rest of the domestic Phase II/III clinical study conducted on cedar pollinosis patients, including children (5-17 years old), was conducted under the following dosage regimen: “Once a day, place one TO-206 tablet under the tongue, hold for 1 minute, and swallow. After that, refrain from gargling, eating, or drinking for 5 minutes. Since the clinical trial was conducted using the above method, it can be said that the actual dosage method is also compliant with the above method.
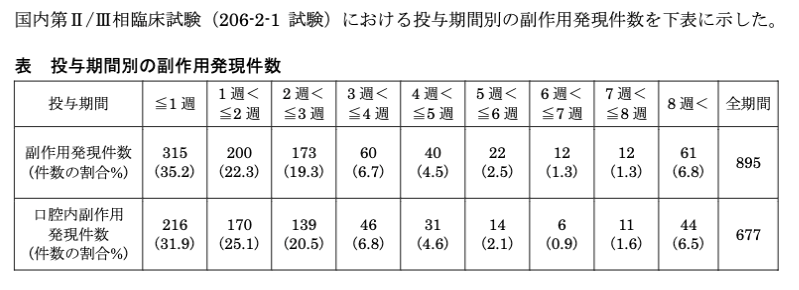
Side effects are most common within the first month of administration.
The three main side effects of sublingual immunization are
- Oral edema, itching, discomfort
- Throat irritation, discomfort
- itching in the ears
The most common of these are oral symptoms, which taper off over time from the start of administration, often within a month.
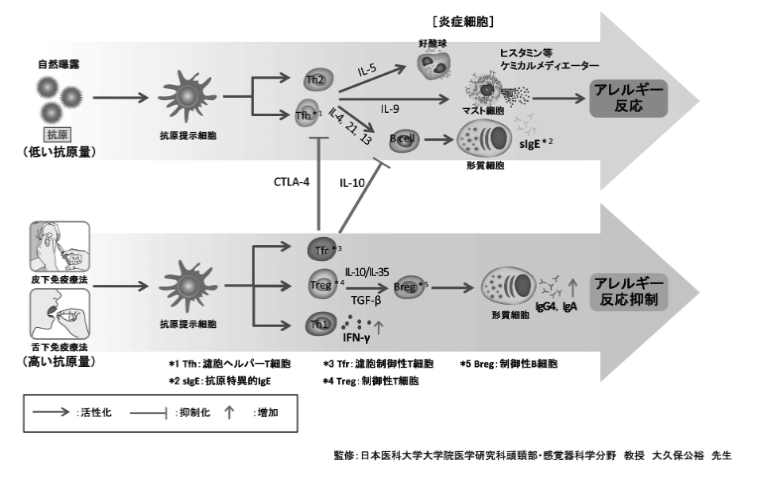
The mechanism of efficacy of desensitization therapy has not been elucidated.
Allergen immunotherapy (desensitization therapy) is a treatment method that increases the body’s tolerance to substances (allergens) that cause allergic reactions, but in fact, the detailed mechanisms of its effectiveness are not fully understood.
The following processes explain why desensitization therapy alleviates allergic reactions, but the details of each mechanism and their interactions are not yet fully understood.
1. allergen capture and early immune response
Sublingually administered allergens are rapidly captured by dendritic cells in the oral submucosa. Dendritic cells function as sentinels (surveillance cells) of the immune system and play an important role in recognizing allergens and transmitting information to other immune cells.
2. modulation of immune response
After processing and presentation of allergens by dendritic cells, the immune response shifts from a Th2-type to a Th1-type response. Normally, allergic reactions are associated with Th2-type immune responses, which promote the production of IgE antibodies and cause allergic symptoms. In desensitization therapy, the promotion of the Th1 response suppresses the activity of the Th2 response, which causes inflammation.
3. induction of regulatory T cells
Treatment increases the number of regulatory T cells (Treg cells). These cells suppress immune responses and contribute to the regulation of allergic reactions by suppressing excessive immune responses.
4. changes in antibody production
Increased allergen-specific IgG and IgA antibodies have been observed. These antibodies play a protective role against allergens and suppress the development of allergic symptoms by blocking the excessive response by IgE.
At the end.
I learned a lot.


