Introduction.
On February 19, 2024, Gartner released a study showing that search engine volume will decline by 25% by 2026 due to the rise of AI chatbots and virtual AI assistants.
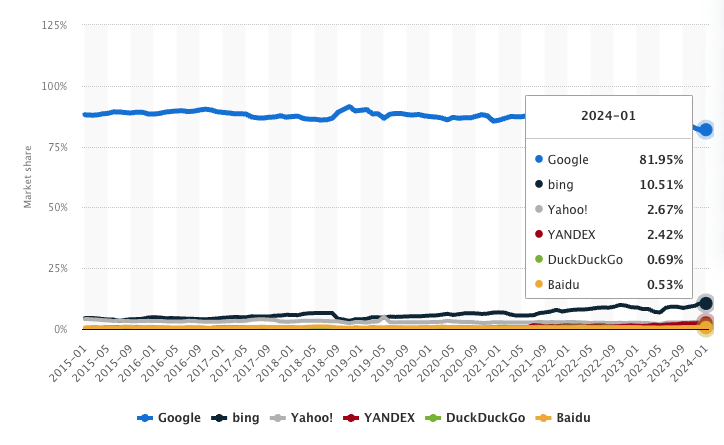
Although Google remains a stronghold in the search engine market, Microsoft’s Bing is on the rise, and Google’s market share has dropped from 90% to nearly 80% in the last five years or so.
This article describes how SEO measures would be affected and how content evaluation criteria would change if we were to enter the age of AI search.
What is AI Chat Search?
For example, an AI chatbot called Perplexity provides an “answer engine” based on a large language model that can retrieve a variety of information in a chat format Perplexity always adds a citation link to which web page information was referenced when generating an answer .
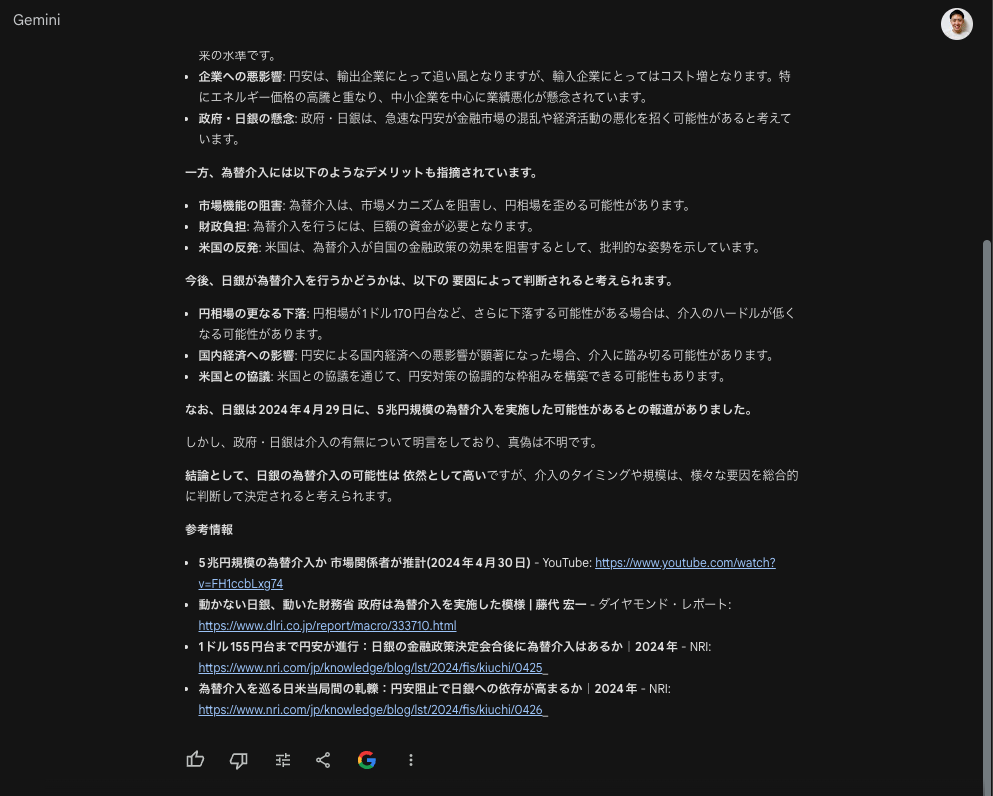
As a test, we asked “Tell me about the possibility of the Bank of Japan’s currency intervention” as a timely matter, and the following response was displayed.
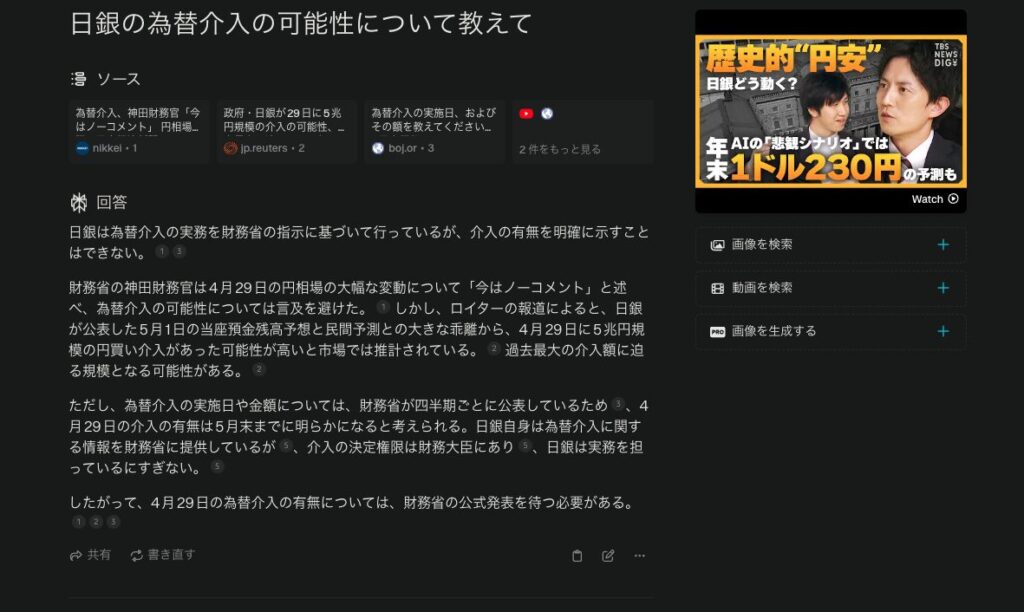
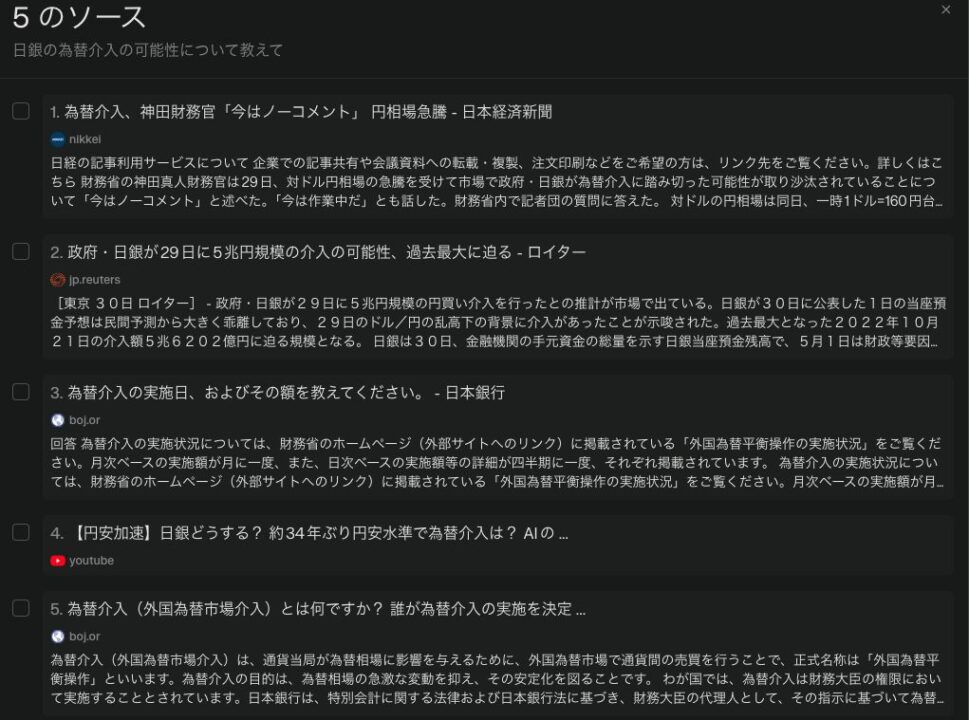
Five sources are shown, including Nikkei, Reuters, and youtube.
The source is attached to the end of the text of the response in the form of a citation number. It is similar to a bibliography when reading a paper.
On the other hand, here is the case of Google: the BOJ’s site, ranked No. 1, displays a general explanation of the BOJ’s currency intervention, but there is no mention of this “possibility of BOJ’s currency intervention” here. This is probably due to keyword mapping by extracting the relevant keywords (BOJ, currency intervention) from the text of the search (i.e., the search results are not based on contextual understanding).
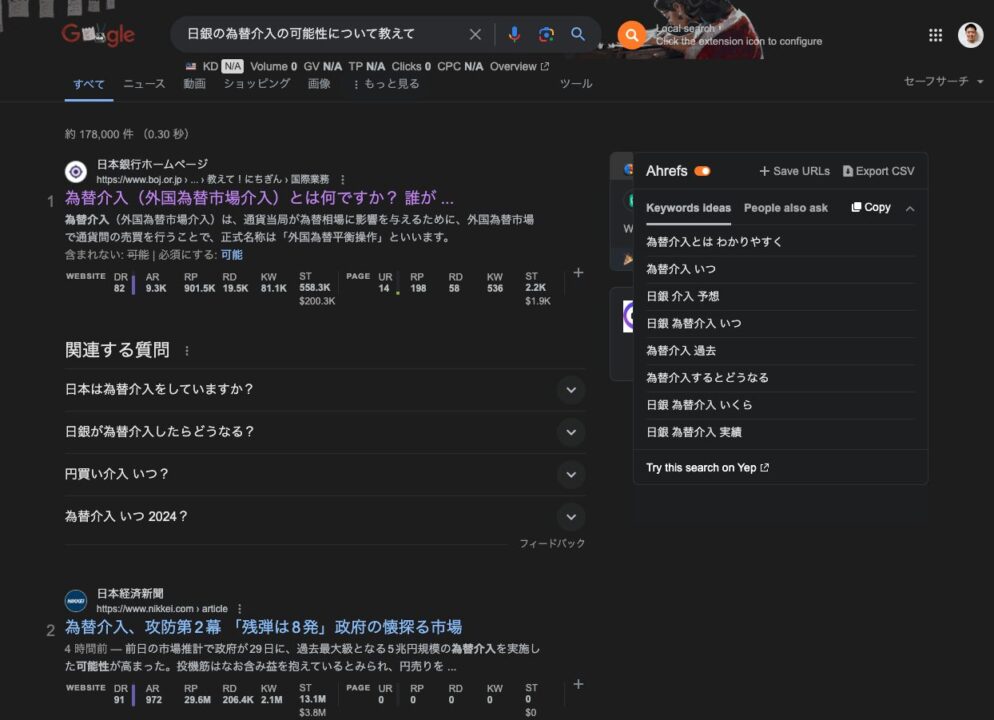
On the other hand, Perplexity shows a similar BOJ site as the fifth source, not the first.
So, as users move from Google search to AI chat search, it will be a battle to get their content into the list of approximately five or so that will appear as citations for answers.
In the case of Google searches, the battle was for one page, or the top 10 results, but the quota is expected to be even tighter.
Incidentally, google’s Gemini AI also shows citations in the AH chat search, but with 4-5.
Changes in SEO: More value placed on quality of content
As noted in the Gardener report mentioned earlier,
Generated AI will lower the cost of content production, which will impact activities such as keyword strategy and domain authority scoring of websites. Search engine algorithms will place even greater emphasis on content quality to offset the vast amount of AI-generated content.
Source: https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2024-02-19-gartner-predicts-search-engine-volume-will-drop-25-percent-by- 2026-due-to-ai-chatbots-and-other-virtual-agents
Google has evolved to evaluate the quality of content more in its battle with SEO companies. Specifically, meta keywords and keyword stuffing, which scatters keywords throughout an article, are no longer effective.
However, titles, meta descriptions, and links are still considered valid, and there is room for improvement in terms of evaluating the quality of content.
While the cost of content generation will drop dramatically with generative AI, it is expected to be flooded with content of dubious authenticity or similar content, so content that is more reliable in its source and differentiated as content will be evaluated. This will be done by Google’s search engine as a countermeasure against generated AI content, as well as AI chat search services like Perplexity, and as an inherent mechanism of LLM.
More specifically, we will look at the criteria for content evaluation.
Criteria for AI content evaluation
- Accuracy: It is important that content is factual. Misinformation and disinformation should be eliminated and only accurate and verified information should be cited.
- Credibility: Reliability of sources is important, and content from scientific studies, public institutions, and recognized experts is preferred.
- Timeliness: Newness of information is also important. Especially in rapidly changing topics, up-to-date information tends to be given priority.
- Comprehensiveness: content that offers different perspectives to answer a user’s question from multiple angles will be valued; such unique content will be valued more because it is better to feed different data from the LLM’s learning perspective.
- Relevance: select information that is most relevant to the user’s question or topic.
We will look at this “relevance” in more detail.
Differences in extraction of related articles in Google search and LLM
Google search engine algorithm
Keyword Matching:
Google search focuses on where and how the keywords entered by the user are used on the web page. The frequency (frequency and density) of the keyword’s appearance on the page, its use in the title tag and metadata, etc. are considered important.
Link Structure Analysis:
The Page Rank algorithm is used to evaluate how well a web page is linked to by other pages. Pages that are linked to many high-quality sites are considered more reliable and relevant.
Analysis of user behavior:
Analyze past user behavior, including click-through rates (CTR), to evaluate which pages actually meet user needs.
Large-scale language model (LLM) using Transformer
To understand LLM, it is necessary to understand the original deep learning model called Transformer and the Attention mechanism. The following video is easy to understand.
With the advent of Transformer, the following major changes have occurred in terms of relevance.
Relevance evaluation based on contextual understanding:
Transformer uses a self-attention mechanism to understand the context of the entire input text. This allows it to go beyond simple keyword matching and capture the meaning and nuances of a sentence.
Semantic Matching:
Determines relevance by identifying phrases and themes that are similar in context and meaning, even if the keywords do not directly match. This allows for a deeper level of textual understanding.
Dynamic Learning and Adaptation:
LLMs have the ability to continuously learn from training data and adapt to new linguistic patterns and expressions. This allows its evaluation accuracy to improve over time; it will go from discrete changes like Google search, with regular algorithm updates and significant changes in search rankings each time, to continuous changes in search rankings based on more dynamic learning.
Differences from the Google Era
In summary, the differences from the Google era include the following
- Changes in SEO keyword strategy: While keyword optimization was important in Google search, AI chat search places more emphasis on contextual understanding and requires keyword-independent natural language processing skills.
- Decreased importance of links: In traditional SEO, links from other sites contributed to improved rankings, but in AI search, the quality of content itself is evaluated more directly, and thus the quality of content is more important than the number of links.
When it comes to AI chat searches, users will not be searching for a list of keywords such as “Bank of Japan currency intervention,” but rather “What are the chances of Bank of Japan currency intervention?” but rather a search (question) with a sentence such as “What is the possibility of BOJ’s currency intervention?
In the Google era, users were mainly using keyword search input, so keyword frequency matching was mainstream, but in the AI chat search era, content that better fits the context will be selected based on users’ natural language search.
It will be more required to provide content that is free of misinformation, described by people and institutions of high authority and expertise, and that corresponds to the latest information and matches the natural language (written) questions of the user.
It all boils down to the obvious and simple statement that we should prepare answers that meet the user’s search (question) needs.
And it is more difficult to do small SEO.



コメント